Qualcomm Dominating In Mobile Processors, Still Powerful in Intellectual Property Rights
You would be not be scolded for not knowing who Qualcomm are. For many years they were basically owners of valuable intellectual property and made money from patents and licensing the rights to use technology from those patents. Revenues in 2014 exceeded $24 billion up from $10 billion just 4 years prior, with net income up to $7.5 billion from $3.25 billion in 2010. Clearly they know what they're doing.
The research and development arm of Qualcomm is still there, but today the intellectual property revenues are just 30 percent of the total revenue of the business. The UMTS interface is part of that and its included in pretty much every smart phone and tablet on the planet.
Qualcomm Has History In Mobile
Unlike Intel trying to make inroads with their Atom brand, Qualcomm chipsets, modems and processors have been inside phones for years already. Engineers who design the phones and OEMs who can have some say over components often like to stick to what they know.
The company and its hardware components have been successfully used for so long that now companies like Intel are the ones that have trouble being trusted. Tried and true wins out over brand new and Qualcomm is tried and true in the mobile market. This places Intel in the AMD position in the PC market which is a position they are completely unaccustomed to.
A case in point is the fact that Qualcomm were the first to develop a 28nm (nanometer) 4G LTE modem which could be included in mobile devices to make 4G mobile telecommunications a reality.
The SnapDragon brand
The SnapDragon line of processors now come included in some of the fastest smart phones and tablets. So much so that some more savvy consumers actually look for the SnapDragon brand and the model of the processor to see exactly what they'll be getting under the hood.
Whilst the Intel Corporation are finally making their own presence known in the mobile market after seemingly being asleep at the PC wheel for the past five years, Qualcomm have been busily taking advantage of their first mover advantage (or at least ahead of Intel advantage). And it shows.
Video Management On The Chip
The collection of systems on a chip (SoCs) products like SnapDragon come with an ARMv7 instruction set making them compatible with operating systems like Android. Most of the SnapDragon processors include circuitry which is capable of decoding HD video content at either 720p or 1080p resolution depending on the processor model. The graphics processor Adreno is integrated into many of the Qualcomm chips provides excellent graphical capabilities. The latest SnapDragon S4 SoCs includes additional support for The Microsoft DirectX 9 and Shader Model 3 software technologies. This ensures that the chipset could power a Windows system. Audio and video encoding is usually included in SnapDragon 200-800 ranges which speeds up device performance with multimedia tasks, and VoIP phone and video calls too.
Communications On The Die, Not Separate
Cellular communications is included on the die with SnapDragon SoCs, so the chipset includes the GPS and GLONASS (Russian GPS that finds a location faster but is less exact), Wi-Fi and Bluetooth technologies which means that an external modem is not required. This combined with the 28 nanometer production in S4 SoCs means that less power is consumed with this circuitry especially without the need for separate modems alongside the processor. The compact, single chipset solution has a great deal of appeal for phone makers.
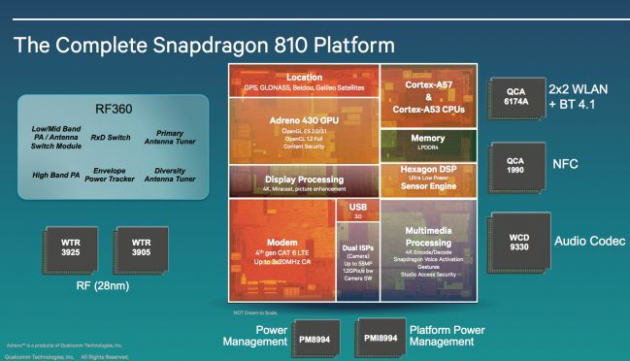
SnapDragon 810 Processor with Category 9 LTE-Advanced
The latest move by Qualcomm is its SnapDragon 810 processor which was announced December 11 which has gone a step further than previously expected with 4G LTE communications. Whilst most smart phones still include a category 3 LTE modem with a maximum speed of 150 megabits per second downstream, they have upped the ante with a category 9 LTE-Advanced processor which offers a maximu of 450 megabits per second downstream and 50 megabits per second upstream. This at a time when most other manufacturers are barely offering a category 6 LTE-Advanced options for 300 megabits per second downstream performance. Qualcomm has leapfrogged right over the competition here.
LG Try Alternatives in Mobile Market
The recent LG G3 includes a LG processor with a separate Intel XMM 7260 LTE-Advanced modem. Whilst this is less efficient, it is being seen by some as LG's attempt to reduce the dependence on a single solution from Qualcomm.
Color E-ink Mirasol Display
Qualcomm is also interested in developing reader technologies to make screens easier on the eyes. Their color e-ink Mirasol display technology is little known about but still under development and has already been included in a few e-reader tablets.
8K TVs and 4K Video Recording
Qualcomm now offers components that can support 8K video resolutions. Their own research has indicated that the center of the retina can perceive resolutions up to 80K.
There are also continued advancements with the recording of video on mobile devices where 4K video can now be recorded using the same power consumption as it takes to record Full HD 1080p.
Planning Ahead 4 Years At A Time
With things like video encoding and decoding, the issue isn't what a processor can do but what algorithms and codecs are being used at the time that the processor is being designed.
Processors use discrete blocks which focus on different abilities. One block could be the ability to work with H.264 video and later an H.265 standard is adopted. At this point a newer H.265 video would not be decoded on the chip and need to be done via software which would be slower. For this reason, Qualcomm technology is designed on the basis that is can be used for up to 4 years but not necessarily longer.
64-Bit Mobile Computing Is The Next Frontier
64-bit processors is the latest development in mobile processing. Apple has it which surprised many in the mobile market but the fact that the company controls both the hardware and the software end of things makes it easier to create fast changes. With Qualcomm, they have to create the chipset first, then liaise with the hardware creators, then the operating system creators and eventually the app makers get notified by Android, Tizen, etc. The whole process is slower but it starts with companies like Qualcomm.